Boeing F/A-18E/F Super Hornet
| F/A-18E/F Super Hornet | |
|---|---|
 U.S. Navy F/A-18F Super Hornet | |
| General information | |
| Type | Carrier-based multirole fighter |
| National origin | United States |
| Manufacturer | McDonnell Douglas (1995–1997) Boeing Defense, Space & Security (1997–present) |
| Status | In service |
| Primary users | United States Navy |
| Number built | ≥632 as of April 2020[1][2] |
| History | |
| Manufactured | 1995–present |
| Introduction date | 2001 (Initial operating capability, IOC)[3] |
| First flight | 29 November 1995 |
| Developed from | McDonnell Douglas F/A-18 Hornet |
| Variants | Boeing EA-18G Growler |
The Boeing F/A-18E and F/A-18F Super Hornet are a series of American supersonic twin-engine, carrier-capable, multirole fighter aircraft derived from the McDonnell Douglas F/A-18 Hornet. The Super Hornet is in service with the armed forces of the U.S., Australia, and Kuwait. The F/A-18E single-seat and F tandem-seat variants are larger and more advanced versions of the F/A-18C and D Hornet, respectively.
A strike fighter capable of air-to-air and air-to-ground/surface missions, the Super Hornet has an internal 20mm M61A2 rotary cannon and can carry air-to-air missiles, air-to-surface missiles, and a variety of other weapons. Additional fuel can be carried in up to five external fuel tanks and the aircraft can be configured as an airborne tanker by adding an external air-to-air refueling system. An electronic warfare variant, the EA-18G Growler, was also developed. Although officially named "Super Hornet", it is commonly referred to as "Rhino" within the U.S. Navy.
Designed and initially produced by McDonnell Douglas, the Super Hornet first flew in 1995. Low-rate production began in early 1997, reaching full-rate production in September 1997, after the merger of McDonnell Douglas and Boeing the previous month. The Super Hornet entered operational service with the United States Navy in 2001, supplanting the Grumman F-14 Tomcat, which was retired in 2006; the Super Hornet has served alongside the original Hornet as well. The F/A-18E/F has been used extensively in combat operations in the Middle East, including the wars in Afghanistan and Iraq, and against the Islamic State and Assad-aligned forces in Syria. The Royal Australian Air Force (RAAF), which has operated the F/A-18A as its main fighter since 1984, ordered the F/A-18F in 2007 to replace its aging General Dynamics F-111C fleet with the RAAF Super Hornets entering service in December 2010.
Development
[edit]Origins
[edit]The Super Hornet is a redesign of the McDonnell Douglas F/A-18 Hornet. The wing and tail configuration trace its origin to a Northrop prototype aircraft, the P-530, c. 1965, which began as a rework of the lightweight Northrop F-5E (with a larger wing, twin tail fins and a distinctive leading edge root extension, or LERX).[4] Later flying as the Northrop YF-17 "Cobra", it competed in the United States Air Force's Lightweight Fighter (LWF) program to produce a smaller and simpler fighter to complement the larger McDonnell Douglas F-15 Eagle; the YF-17 lost the competition to the YF-16.[5]

The Navy directed that the YF-17 be redesigned into the larger F/A-18 Hornet to meet a requirement for a multi-role fighter (VFAX) to complement the larger and more expensive Grumman F-14 Tomcat serving in fleet defense interceptor and air superiority roles. The Hornet proved to be effective but limited in combat radius. The concept of an enlarged Hornet was first proposed in the 1980s, which was marketed by McDonnell Douglas as Hornet 2000. The Hornet 2000 concept was an advanced F/A-18 with a larger wing and a longer fuselage to carry more fuel and more powerful engines.[5][6]
The end of the Cold War led to a period of military budget cuts and considerable restructuring. At the same time, U.S. Naval Aviation faced a number of problems. The McDonnell Douglas A-12 Avenger II Advanced Tactical Aircraft (ATA) was canceled in 1991 after the program ran into serious problems; it was intended to replace the obsolete Grumman A-6 Intruder.[7] The Navy then embarked on another clean-sheet attack aircraft program called the Advanced-Attack (A-X), but also considered updating an existing design for an interim capability until A-X could be fielded.[8] Meanwhile, McDonnell Douglas had proposed the "Super Hornet" (initially "Hornet II" and later "Hornet 2000" in the 1980s), an improvement of the successful previous F/A-18 models,[6] which could serve as an alternate replacement for the A-6 Intruder or an interim aircraft for A-X; the design would also address some of the limitations of the Hornet, such as insufficient bringback capability, or the ability to recover unused weapons aboard aircraft carriers.[9] The next-generation Hornet design proved more attractive than Grumman's Quick Strike upgrade to the F-14 Tomcat, which was regarded as an insufficient technological leap over existing F-14s and was opposed by the Secretary of Defense Dick Cheney. Furthermore, the A-X, which had evolved into the A/F-X (Advanced Attack/Fighter) due to added fighter capabilities, was canceled in the 1993 Bottom-Up Review as the Super Hornet was viewed as a more attractive low-risk approach to a clean-sheet design due to post-Cold War budget reductions.[10]
At the time, the Grumman F-14 Tomcat was the Navy's primary air superiority fighter and fleet defense interceptor. Cheney described the F-14 as 1960s technology, and drastically cut back F-14D procurement in 1989 before cancelling production altogether in 1991, in favor of the updated F/A-18E/F.[11][12] The decision to replace the Tomcat with an all-Hornet Carrier Air Wing was controversial; Vietnam War ace and Congressman Duke Cunningham criticized the Super Hornet as an unproven design that compromised air superiority.[10][13] In 1992, the Navy canceled the Navy Advanced Tactical Fighter (NATF), which would have been a navalized variant of the Air Force's Lockheed Martin F-22 Raptor to complement the A-12, due to escalating costs.[5] As a cheaper alternative to NATF, Grumman proposed substantial improvements to the F-14 beyond Quick Strike, but Congress rejected them as too costly and reaffirmed its commitment to the less expensive F/A-18E/F. Originally viewed as an interim for A-X or A/F-X, the Super Hornet would become the mainstay of the Carrier Air Wing.[14]
Testing and production
[edit]
The Super Hornet was first ordered by the U.S. Navy in 1992, and the total Engineering and Manufacturing Development (EMD) cost was capped at $4.88 billion in FY 1990 dollars (~$10.1 billion in 2023).[15] The Navy retained the F/A-18 designation to help sell the program to Congress as a low-risk "derivative", though the Super Hornet is largely a new aircraft. To some extent, the design of the F/A-18E/F was driven by a more cautious development approach favoring incremental improvements over the F/A-18C/D, affordability, and reliability at the expense of raw performance. The Hornet and Super Hornet share many characteristics, including avionics, ejection seats, radar, armament, mission computer software, and maintenance/operating procedures. The Super Hornet's F414 engines were derived from the Hornet's F404 while also incorporating advances developed for the A-12's F412. The initial F/A-18E/F retained most of the avionics systems from the F/A-18C/D's configuration at the time to reduce upfront development costs.[16][5] The design would be expanded in the Super Hornet with an empty weight slightly greater than the F-15C. The design service life was 6,000 flight hours.[17]
The Super Hornet first flew on 29 November 1995.[5] Initial production on the F/A-18E/F began in 1995. Flight testing started in 1996 with the F/A-18E/F's first carrier landing in 1997.[5] Low-rate production began in March 1997[18] with full production beginning in September 1997.[19] Testing continued through 1999, finishing with sea trials and aerial refueling demonstrations, as well as design modifications to resolve "wing drop" and possible stores release interference. Testing involved 3,100 test flights covering 4,600 flight hours.[6] The Super Hornet underwent U.S. Navy operational tests and evaluations in 1999,[20] and was approved in February 2000.[21]

With the retirement of the F-14 in 2006, all of the Navy's combat jets have been Hornet variants until the F-35C Lightning II entered service. The F/A-18E single-seat and F/A-18F two-seat aircraft took the place of the F-14 Tomcat, A-6 Intruder, Lockheed S-3 Viking, and KA-6D aircraft. An electronic warfare variant, the EA-18G Growler, replaced the EA-6B Prowler. The Navy calls this reduction in aircraft types a "neck-down". During the Vietnam War era, the Super Hornet's roles were performed by a combination of the A-1/A-4/A-7 (light attack), A-6 (medium attack), F-8/F-4 (fighter), RA-5C (recon), KA-3/KA-6 (tanker), and EA-6 (electronic warfare). It was anticipated that $1 billion in fleetwide annual savings would result from replacing other types with the Super Hornet.[22] The Navy considers the Super Hornet's acquisition a success, meeting cost, schedule, and weight (400 lb, 181 kg) below requirement threshold limits.[3]
The total Super Hornet procurement number would fluctuate considerably throughout its production run. The 1997 Department of Defense (DoD) Quadrennial Defense Review cut the originally planned number of around 1,000 by nearly half. By October 2008, Boeing had delivered 367 Super Hornets to the U.S. Navy, but the service was still experiencing a strike fighter shortfall as older aircraft types retired and the procurement rate was not sufficient to replenish the carrier air wings, especially with ongoing combat operations in Iraq and Afghanistan as well as substantial delays with the F-35 program.[23][24] In 2006, the Navy was 60 fighters below its validated requirement.[25][26][27] The FY2010 budget bill authorized a multiyear purchase agreement for additional Super Hornets, finalized on 28 September 2010, that reportedly saved $600 million over individual yearly contracts.[28][29] This contract for 66 Super Hornets and 58 Growlers was intended to mitigate a four-year delay in the F-35 program.[30] In 2019, Boeing received a $4 billion contract to deliver 78 Block III Super Hornets for the Navy through fiscal 2021. The Navy plans to sign year to year contracts to convert all of its Block II aircraft to Block III variants through 2033.[31] As the F-35 began entering service, Boeing announced plans to end Super Hornet production in 2025, later extended to 2027 with an additional 17 orders from the U.S. Navy.[32][33]
Improvements and changes
[edit]The Block II Super Hornet incorporates an improved active electronically scanned array (AESA) radar, larger displays, the joint helmet mounted cueing system, and several other avionics replacements.[34][35] Avionics and weapons systems that were under development for the prospective production version of the Boeing X-32 were used on the Block II Super Hornet.[36] New-build aircraft received the APG-79 AESA radar beginning in 2005.[34] In January 2008, it was announced that 135 earlier production aircraft were to be retrofitted with AESA radars.[37]
In 2008, Boeing discussed the development of a Super Hornet Block III[38] with the U.S. and Australian military, featuring additional stealth capabilities and extended range. The airframe is strengthened to increase service life to 10,000 flight hours, and some Block II aircraft can be modified to achieve this as well.[39][40] In 2010, Boeing offered prospective Super Hornet customers the "International Roadmap", which included conformal fuel tanks, enhanced engines, an enclosed weapons pod (EWP), a next-generation cockpit, a new missile warning system, and an internal infrared search and track (IRST) system; the IRST would later be mounted on the centerline external tank.[41][42] The EWP has four internal stations for munitions, a single aircraft can carry a total of three EWPs, housing up to 12 AMRAAMs and 2 Sidewinders.[43][44] The next-generation cockpit features a 19 x 11-inch touch-sensitive display.[45] In 2011, Boeing received a US Navy contract to develop a new mission computer.[46]

In 2007, Boeing stated that a passive Infrared Search and Track (IRST) sensor would be an available future option. The sensor, mounted in a modified centerline fuel tank, detects long wave IR emissions to spot and track targets such as aircraft;[47] combat using the IRST and AIM-9X Sidewinder missiles is immune to radar jamming.[48] In May 2009, Lockheed Martin announced its selection by Boeing for the IRST's technology development phase,[49] and a contract followed in November 2011.[50] As of September 2013[update], a basic IRST would be fielded in 2016 and a longer-range version in 2019. The sensor would be designated the AN/ASG-34(V) IRST21. An F/A-18F performed a flight equipped with the IRST system in February 2014, and Milestone C approval authorizing low-rate initial production (LRIP) was granted in December 2014. Due to sequestration cuts in 2013 as well as production quality issues, caused years of delay.[48][51]
Advanced Super Hornet
[edit]Boeing and Northrop Grumman self-funded a prototype of the Advanced Super Hornet.[52] The prototype features a 50% reduction in frontal radar cross-section (RCS), conformal fuel tanks (CFT), and an enclosed weapons pod.[53][54] Features could also be integrated onto the EA-18G Growler: using CFTs on the EA-18G fleet was speculated as useful for relieving underwing space and lowering the drag margin for the Next Generation Jammer.[55][56] Flight tests of the Advanced Super Hornet began on 5 August 2013 and continued for three weeks, testing the performance of CFTs, the enclosed weapons pod (EWP), and signature enhancements.[57] The U.S. Navy was reportedly pleased with the Advanced Super Hornet's flight test results, and hopes it will provide future procurement options.[58] Although the Advanced Super Hornet was not pursued, many elements would be transferred to the Block III.[59]
In 2013, the U.S. Navy was considering the widespread adoption of CFTs, which would allow the Super Hornet to carry 3,500 lb (1,600 kg) of additional fuel. Budgetary pressures from the F-35C Lightning II and Pacific region operations were cited as reasons supporting the use of CFTs. Flight testing demonstrated CFTs could slightly reduce drag while expanding the combat range by 260 nautical miles (300 mi; 480 km).[60] The prototype CFT weighed 1,500 lb (680 kg), while production CFTs are expected to weigh 870 lb (390 kg). Boeing stated that the CFTs do not add any cruise drag but acknowledged a negative impact imposed on transonic acceleration due to increased wave drag. General Electric's enhanced performance engine (EPE), increasing the F414-GE-400's power output by 20%, was suggested as a mitigating measure.[61] In 2021, the U.S. Navy halted plans to fit CFTs as standard on all Block III Super Hornets due to cost, schedule, and performance issues.[62]
In 2009, development commenced on several engine improvements, including greater resistance to foreign object damage, reduced fuel burn rate, and potentially increased thrust of up to 20%.[63][64] In 2014, Boeing revealed a Super Hornet hybrid concept, equipped with the EA-18G Growler's electronic signal detection capabilities to allow for targets engagement using the receiver; the concept did not include the ALQ-99 jamming pod. Growth capabilities could include the addition of a long-range infrared search and track sensor and new air-to-air tracking modes.[65]
Design
[edit]Overview
[edit]
The Super Hornet is largely a new aircraft at about 20% larger, 7,000 lb (3,200 kg) heavier empty weight, and 15,000 lb (6,800 kg) heavier maximum weight than the original Hornet. The Super Hornet carries 33% more internal fuel, increasing mission range by 41% and endurance by 50% over the "Legacy" Hornet. The empty weight of the Super Hornet is about 11,000 lb (5,000 kg) less than that of the F-14 Tomcat which it replaced, while approaching, but not matching, the F-14's payload and range.[66][N 1] Although lacking some of the F-14's raw performance, the F/A-18E/F has much better handling characteristics and controllability and was also significantly more reliable and affordable to operate. With the Super Hornet being significantly heavier than the legacy Hornet, the catapult and arresting systems must be set differently. To aid safe flight operations and prevent confusion in radio calls, the Super Hornet is informally referred to as the "Rhino" to distinguish it from earlier Hornets partly because of the AN/APX-111 "pizza box" IFF antenna on the nose. (The "Rhino" nickname was previously applied to the McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II, which was retired from US Navy combat use in 1987.)[67]
The Super Hornet, unlike the previous Hornet, can be equipped with an aerial refueling system (ARS) or "buddy store" for the refueling of other aircraft,[68] filling the tactical airborne tanker role the Navy had lost with the retirement of the KA-6D and Lockheed S-3B Viking tankers. The ARS includes an external 330 US gal (1,200 L) tank with hose reel on the centerline, along with four external 480 US gal (1,800 L) tanks and internal tanks, for a total of 29,000 lb (13,000 kg) of fuel on the aircraft.[68][69] On typical missions a fifth of the air wing is dedicated to the tanker role, which consumes aircraft fatigue life expectancy faster than other missions.[70] It most commonly uses JP-5 jet fuel.[71]
Airframe changes
[edit]
The forward fuselage is unchanged, but the remainder of the aircraft shares little with earlier F/A-18C/D models. The fuselage was stretched by 34 in (86 cm) to make room for fuel and future avionics upgrades and increased the wing area by 25%,[72] yet the Super Hornet has 42% fewer structural parts than the original Hornet.[73] The wings have a dogtooth extension and a strip of porous surface at the folding joint to mitigate "wing drop".[N 2] The General Electric F414 engine, developed from the Hornet's F404, has 35% additional thrust over most of the flight envelope and is rated at 22,000 lbf (98 kN) in afterburner.[72][74] The Super Hornet can return to an aircraft carrier with a larger load of unspent fuel and munitions than the Hornet; this ability is known as "bringback", which for the Super Hornet is in excess of 9,000 lb (4,100 kg).[75]

Other differences include larger caret inlets with fixed ramps for the more powerful engines and two extra wing hard points for payload (for a total of 11), retaining previous hardpoints on the bottom centerline, wingtips, and two conformal fuselage positions.[76] Among the most significant aerodynamic changes are the enlarged leading edge extensions (LEX) that provide improved vortex lifting characteristics in high angle of attack maneuvers, and reduce the static stability margin to enhance pitching characteristics. This modification results in pitch rates in excess of 40 degrees per second, and high resistance to departure from controlled flight.[77] Due to concerns over released stores potentially striking the airframe due to early wind tunnel testing, all underwing pylons are canted outwards slightly; although this was later determined to be unnecessary, production tooling had already been adjusted so the canted pylons remained to save development costs and revalidating all flight testing. While the effects are marginal for cruise drag, they are more substantial for transonic and supersonic drag.[78]
Radar signature reduction measures
[edit]
Survivability is a key feature of the Super Hornet. The U.S. Navy took a "balanced approach" to survivability in its design.[79] It does not rely primarily on low-observability technology, but rather adopts improvements to its radar signature alongside other innovations; incorporating more advanced electronic warfare capabilities, reduced ballistic vulnerability, and greater employment of standoff weapons to collectively enhance crew and aircraft safety.[79][80] While the F/A-18E/F is not a stealth fighter like the F-22, it does have a frontal radar cross-section (RCS) an order of magnitude smaller than prior generation fighters.[81] Additional changes for reducing RCS can be installed on an as-needed basis.[82]
The F/A-18E/F's RCS is reduced greatly from some aspects, mainly the front and rear.[5] The design of the caret engine inlets reduces the aircraft's frontal radar cross-section, with the alignment of the leading edges of the inlets designed to scatter radiation to the sides. Fixed fanlike reflecting structures in the inlet tunnel divert radar energy away from the rotating fan blades.[81] The Super Hornet also makes considerable use of panel joint serration and edge alignment to direct reflected waves away from the aircraft in uniformly narrow angles. Considerable attention is paid to the removal or filling of unnecessary surface join gaps and resonant cavities. Where the F/A-18A-D used grilles to cover various accessory exhaust and inlet ducts, the F/A-18E/F uses perforated panels that appear opaque to radar waves at the frequencies used.[5]
Avionics
[edit]
Initially, the Super Hornet's avionics and software had a 90% commonality with that of the F/A-18C/D fleet at the time.[74] Differences include an up-front touchscreen control display; a large multipurpose color liquid-crystal display; and a fuel display.[74] The Super Hornet has a quadruplex digital fly-by-wire system,[83] as well as a digital flight-control system that detects and corrects for battle damage.[77] Initial production models used the APG-73 radar, later replaced by the AN/APG-79 active electronically scanned array (AESA).[34][35] The AN/ASQ-228 ATFLIR (Advanced Targeting Forward Looking InfraRed), is the main electro-optical sensor and laser designator pod for the Super Hornet. The communications equipment consist of an AN/ARC-210 VHF/UHF radio[84] and a MIDS-JTRS low volume terminal for HAVE QUICK, SINCGARS and Link 16 connectivity.
The defensive countermeasures of Block I aircraft includes the AN/ALR-67(V)3 radar warning receiver, the AN/ALE-47 countermeasures dispenser, the AN/ALE-50 towed decoy and the AN/ALQ-165 Airborne Self-Protect Jammer (ASPJ). Block II aircraft replace the ALQ-165 with the AN/ALQ-214 Integrated Defensive Countermeasures (IDECM) system, consisting of internally mounted threat receivers and optional self-protection jammers. Interior and exterior lighting on the Block II was changed to allow the use of night vision devices. The older ALE-50 decoys are being replaced by ALE-55 towed decoys, which can transmit jamming signals based on data received from the IDECM.[citation needed] The improved AN/ALQ-214 jammer was added on Block II aircraft.[35]
Block II aircraft were fitted with the AN/APG-79 AESA radar, capable of executing simultaneous air-to-air and air-to-ground attacks, and providing higher quality high-resolution ground mapping at long standoff ranges.[85] The AESA radar can also detect smaller targets, such as inbound missiles[86] and can track air targets beyond the range of the aircraft's air-to-air missiles.[87] VFA-213, the first squadron to fly AESA-equipped Super Hornets, became "safe for flight" (independently fly and maintain the F/A-18F) on 27 October 2006.[88] The first Super Hornet upgraded with the Joint Helmet Mounted Cueing System (JHMCS) was delivered to VFA-213 on 18 May 2007.[89] The JHMCS provides multi-purpose situational awareness, which includes high-off-boresight missile cuing. The Shared Reconnaissance Pod (SHARP) is a high-resolution, digital tactical aerial reconnaissance system that features advanced day/night and all-weather capability.[90] The Multifunctional Information Distribution System low volume communication terminal is being upgraded with the MIDS-JTRS system,[91] which will allow a tenfold increase in bandwidth as well as compatibility with the Joint Tactical Radio System standards.[92] For passive infrared detection and targeting, the aircraft can carry the AN/ASG-34(V) IRST21 contained in a modified centerline FPU-13 external fuel tank; the sensor occupies for forward portion of the tank, reducing its capacity to 330 gallons.[51]
Development of Block III avionics upgrades has been underway as of April 2019.[93]
Operational history
[edit]United States Navy
[edit]
In 1999, the Super Hornet entered fleet service with the U.S. Navy.[94][95] It achieved initial operating capability (IOC) in September 2001 with the U.S. Navy's Strike Fighter Squadron 115 (VFA-115) at Naval Air Station Lemoore, California.[3] VFA-115 was also the first unit to take their F/A-18s into combat. On 6 November 2002, two F/A-18Es conducted a "Response Option" strike in support of Operation Southern Watch on two surface-to-air missile launchers at Al Kut, Iraq and an air defense command and control bunker at Tallil air base. One of the pilots dropped 2,000 lb (910 kg) JDAM bombs from the Super Hornet for the first time during combat.[96]
In support of Operation Iraqi Freedom (Iraq War), VFA-14, VFA-41 and VFA-115 flew close air support, strike, escort, SEAD and aerial refueling sorties. Two F/A-18Es from VFA-14 and two F/A-18Fs from VFA-41 were forward deployed to Abraham Lincoln. The VFA-14 aircraft flew mostly as aerial refuelers and the VFA-41 fighters as Forward Air Controller (Airborne) or FAC(A)s. On 6 April 2005, VFA-154 and VFA-147 (the latter squadron then still operating F/A-18Cs) dropped two 500-pound (230 kg) laser-guided bombs on an enemy insurgent location east of Baghdad.[citation needed] On 8 September 2006, VFA-211 F/A-18Fs expended GBU-12 and GBU-38 bombs against Taliban fighters and Taliban fortifications west and northwest of Kandahar. This was the first time the unit had participated in an active combat capacity using the Super Hornet.[97][98]
During the 2006–2007 cruise with Dwight D. Eisenhower, VFA-103 and VFA-143 supported Operations Iraqi Freedom, Enduring Freedom and operations off the Somali coast. Alongside "Legacy Hornet" squadrons, VFA-131 and VFA-83, they dropped 140 precision guided weapons and performed nearly 70 strafing runs.[99] The Super Hornet can operate from the French aircraft carrier Charles de Gaulle.[100]

On 7 August 2014, U.S. defense officials announced they had been authorized to launch bombing missions upon Islamic State (IS) forces in northern Iraq. The decision to take direct action was made to protect U.S. personnel in the city of Irbil and to ensure the safety of transport aircraft making airdrops to Yazidi civilians. Early on 8 August, two Super Hornets took off from George H.W. Bush and dropped 500 lb laser-guided bombs on a "mobile artillery piece" the militants had been using to shell Kurdish forces defending the city.[101][102] Later that day, four more aircraft struck a seven-vehicle convoy and a mortar position.[103]

On 18 June 2017, a U.S. Navy F/A-18E shot down a Syrian Air Force Su-22 fighter-bomber that allegedly had bombed a position held by U.S.-supported Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF) near Tabqa; the Syrian government claimed the Su-22 was bombing an IS position. This was the first aerial kill of a crewed aircraft by an American fighter since 1999, the first by the Navy since the 1991 Persian Gulf War, the first kill by a Super Hornet, and the third kill by an F/A-18.[104] An E-3 Sentry issued several warnings to the Su-22 and, after it dropped bombs near SDF fighters, the F/A-18E, piloted by Lieutenant Commander Michael "MOB" Tremel, a pilot assigned to Strike Fighter Squadron 87 aboard the carrier George H.W. Bush, independently chose to shoot it down based on established rules of engagement. The F/A-18E first missed with an AIM-9X Sidewinder, then hit the Su-22 with an AIM-120 AMRAAM; the encounter lasted eight minutes.[105]
In 2018, Boeing was awarded a contract to convert nine single-seat F/A-18E Super Hornets and two F/A-18F two-seaters for Blue Angels use; these were to be completed by 2021.[106]
On 26 December 2023, Super Hornets from USS Dwight D. Eisenhower, along with the accompanying destroyer USS Laboon, destroyed 12 attack drones, three anti-ship missiles and two ground attack cruise missiles fired by Houthi forces in the southern Red Sea.[107] Around 2:30 AM local time on 12 January 2024, Houthi targets were struck by U.S. Navy, USAF, and RAF forces in response to Houthi attacks against commercial shipping in the Red Sea. Super Hornets from Dwight D. Eisenhower took part in the strikes, which in total hit 60 targets at 16 locations using over 100 PGMs of various types.[108][109][110]
Royal Australian Air Force
[edit]On 3 May 2007, the Australian Government signed a $2.9 billion contract to acquire 24 F/A-18Fs as an interim replacement for the Royal Australian Air Force's (RAAF) aging F-111s.[111] It was reported that the order would also address any difficulties that might be caused by a need to quickly replace the RAAF's existing fleet of classic F/A-18A/B Hornets in the event of delays to the F-35 program.[112] The total cost of the purchase, with training and support over 10 years, was expected to be A$6 billion (US$4.6 billion).[113]

The order was controversial; Air Vice Marshal (retired) Peter Criss, said that he was "absolutely astounded" that $6 billion would be spent on an interim aircraft,[115] and cited the US Senate Armed Services Committee, to the effect that the "excess power" of the Block I Super Hornet was inferior to that of the MiG-29 and Su-30, both of which were being operated by, or were on order for, air forces in South East Asia.[116] Another former senior RAAF officer, Air Commodore (ret.) Ted Bushell stated that the F/A-18F could not perform the strategic deterrent/strike role of the F-111C and the latter could continue to operate until 2020 at least.[115] On 31 December 2007, the new Australian Labor government announced a review of the RAAF's aircraft procurement plans citing suitability concerns, the lack of a proper review process, and beliefs that an interim fighter was not needed.[117]
On 17 March 2008, the Government announced that it would proceed to acquire 24 F/A-18Fs.[2] Defence Minister Joel Fitzgibbon called the Super Hornet an "excellent aircraft",[2] and indicated that costs and logistical factors contributed to the decision: the F-111's retirement was "irreversible"; "only" the F/A-18F could meet the timeframe and that termination involved "significant financial penalties and create understandable tensions between the contract partners."[118][119] The Block II aircraft offered include installed engines and six spares, APG-79 AESA radars, Link 16 connectivity, LAU-127 guided missile launchers, AN/ALE-55 fiber optic towed decoys and other equipment.[120] On 27 February 2009, Fitzgibbon announced that 12 of the 24 F/A-18Fs would be wired on the production line for future modification as Boeing EA-18G Growlers at an additional cost of A$35 million. The final decision on the EA-18G conversion, at a cost of A$300 million, would be made in 2012.[121]

The first RAAF F/A-18F made its first flight from Boeing's factory in St. Louis, Missouri, on 21 July 2009.[122] RAAF crews began training in the U.S. in 2009. The first five F/A-18Fs arrived at their home base, RAAF Base Amberley in Queensland, on 26 March 2010;[123] and were joined by six more aircraft on 7 July 2010.[124] After four more aircraft arrived in December 2010, the first RAAF F/A-18F squadron was declared operational on 9 December 2010.[125]
In 2008, U.S. export approval was sought for EA-18G Growlers.[126] In December 2012, Australia sought cost information on acquiring a further 24 F/A-18Fs, which may be bought to avoid a capability gap due to F-35 delays.[127] In February 2013, the U.S. Defense Security Cooperation Agency notified Congress of a possible Foreign Military Sale to Australia for up to 12 F/A-18E/Fs and 12 EA-18Gs with associated equipment, training and logistical support.[128] In May 2013, Australia announced the order of 12 new EA-18Gs instead of converting any F/A-18Fs.[129] In June 2014, Boeing received a contract for 12 EA-18Gs; the first was rolled out on 29 July 2015.[130][131]
On 24 September 2014, eight RAAF F/A-18Fs, along with a KC-30A tanker, an early warning aircraft, and 400 personnel arrived in the United Arab Emirates to take part in operations against Islamic State (IS) militants.[132] On 5 October 2014, the RAAF officially started combat missions over Iraq using a pair of F/A-18Fs armed with GPS guided bombs, they returned safely to base without attacking targets.[133][134] On 8 October 2014, an RAAF F/A-18F conducted its first attack, dropping two bombs on an ISIL facility in northern Iraq.[135] In 2017, EA-18Gs replaced No. 6 Squadron RAAF's F/A-18Fs, which were then transferred to No. 1 Squadron RAAF.[136]
On 8 December 2020, F/A-18F A44-223 rolled into a ditch while attempting to take off at RAAF Base Amberley, the crew ejected. An eyewitness reportedly observed smoke from one of the engines.[137] A day after the incident, the RAAF grounded the fleet of 24 Super Hornets and 11 Growlers while the incident was investigated.[138] The cause was determined to be pilot error. The Super Hornet was repaired, and returned to service in mid-2021.[139]
Kuwait Air Force
[edit]In May 2015, the Kuwait Air Force was reportedly planning to order 28 F/A-18E/Fs with options for an additional 12.[140] However, in June 2015, it was reported that Kuwait was considering a split purchase between the Eurofighter Typhoon and the F/A-18E/F.[141] On 11 September 2015, Kuwait signed an agreement for 28 Eurofighters.[142] In November 2016, a proposed Kuwaiti sale of 32 F/A-18E and 8 F/A-18F fighters, armaments, and associated equipment was approved by the U.S. State Department.[143][144]
In June 2018, the Kuwaiti Government ordered 22 F/A-18Es and 6 F/A-18Fs via a US$1.5 billion contract. All aircraft were scheduled to be delivered by January 2021,[145] but were later rescheduled to be delivered in 2021 due to the COVID-19 pandemic.[146]
Potential operators
[edit]Boeing has pitched the F/A-18E/F to numerous countries, particularly those that operate the legacy Hornet as it was supposed to be a "logical progression from the Hornet to the [Super Hornet], with its logistics, weaponry and training commonalities". So far only the US Navy, Australia, and Kuwait have ordered and received the Super Hornet.[147]
Malaysia
[edit]Boeing offered Malaysia Super Hornets as part of a buy-back package for its existing Hornets in 2002. However, the procurement was halted in 2007 after the government decided to purchase the Sukhoi Su-30MKM instead; Chief Gen. Datuk Nik Ismail Nik Mohamaed of the Royal Malaysian Air Force (RMAF) indicated that the air force had not planned to end the Super Hornet buy, stating that such fighters were needed.[148] Separately, the Super Hornet is a contender for the MRCA program, under which the RMAF seek to equip three squadrons with 36 to 40 new fighters with an estimated budget of RM6 billion to RM8 billion (US$1.84 billion to US$2.46 billion). Other competitors are the Eurofighter Typhoon, Dassault Rafale and Saab JAS 39 Gripen.[149]
Failed bids
[edit]Belgium
[edit]On 12 March 2014, Belgian newspaper De Morgen reported that Boeing is in talks with the Belgian Ministry of Defence about the Super Hornet as a candidate to replace Belgium's aging F-16 fleet.[150] In April 2017, Boeing announced it would not compete in the competition, citing it "does not see an opportunity to compete on a truly level playing field".[151][152] On 25 October 2018, Belgium officially selected the offer for 34 F-35As to replace its fleet of around 54 F-16s.[153][154]
Brazil
[edit]Boeing proposed the Super Hornet to the Brazilian government in response to an initial requirement for 36 aircraft, with a potential total purchase of 120 examples. In October 2018, the Super Hornet was reportedly selected as one of three finalists in Brazil's fighter competition.[24][155] However, news of National Security Agency spying on Brazilian leaders caused animosity between Brazil and the US.[156] Brazil eventually dropped the Super Hornet from its final list and selected the Saab JAS 39 Gripen in December 2013.[157]
Canada
[edit]The Super Hornet was a contender to replace the CF-18 Hornet, a version of the F/A-18A and B models, operated by the Royal Canadian Air Force. Like the older Hornet, the Super Hornet's design is well-suited to Northern Canada's rugged forward operational airfields, while its extended range removes its predecessor's main deficiency while commonalities enable a straightforward transition.[158] In 2010, Canada decided on sole source selection of the F-35A. Boeing claimed that Canada had ignored the Super Hornet's radar cross-section characteristics during evaluation.[159] By April 2012, Canada was reportedly reviewing its F-35 procurement.[160] In September 2013, Boeing provided Canada with data on its Advanced Super Hornet, suggesting that 65 aircraft would cost $1.7 billion less than an F-35 fleet. The US Navy buys Super Hornets for $52 million per aircraft, while the advanced model costs $6–$10 million more per aircraft, dependent on options selected.[161]
The Liberal government elected in 2015 indicated that it would launch a competition to replace the CF-18 fleet. During the election, Liberal Leader Justin Trudeau stated that his government would not buy the F-35.[162] On 22 November 2016, the government announced its intention to acquire 18 Super Hornets on an interim basis.[163] In September 2017, the U.S. State Department granted Canada permission to buy 10 F/A-18Es and 8 F/A-18Fs (or EA-18Gs) along with supporting equipment, spares, and armaments; the agreed cost totaled CA$1.5 billion, or about CA$83.3 million per aircraft, adding the supporting equipment, training, spares, and weapons increased the acquisition cost to CA$6.3 billion.[164] However, Canadian Prime Minister Justin Trudeau warned that the pending Super Hornet sale, along with a possible sale of another 70, was adversely affected by Boeing's actions against Bombardier Aerospace,[164] such as a complaint to the US government over the sale of CSeries airliners to Delta Air Lines at unduly low prices; in September 2017, the U.S. Department of Commerce proposed a 219% tariff on CSeries imported into the US.[165][166] In January 2018, the USITC commissioners unanimously ruled against Boeing that the U.S. industry is not threatened and no duties will be imposed.[167]
In late 2017, the Canadian Government agreed with Australia to purchase 18 used F/A-18 Hornets as an interim measure.[168] Boeing confirmed its bid for the Advanced Fighter Program, likely offering a mix of 88 F/A-18E/F Advanced Super Hornets (Block III) and Boeing EA-18G Growlers.[169][170] On 25 November 2021, Reuters reported that Boeing is out of the competition since its fighter proposal does not meet requirements[171] with the F-35 and Saab JAS 39 Gripen remaining in competition.[172][173]
Denmark
[edit]In 2008, the Royal Danish Air Force was offered the F/A-18E/F Super Hornet as one of three fighters in a Danish competition to replace 48 F-16AM/BMs.[174][175] The other contenders were the F-35A Joint Strike Fighter and the Eurofighter Typhoon. Denmark is a level-3 partner in the JSF program. The final selection was originally planned for mid-2015 where 24 to 30 fighters were expected.[176] In April 2014, the Danish Ministry of Defence handed over a Request for Binding Information (RBI) that specifically listed the F/A-18F two-seat variant.[177] In December 2015, the decision was postponed to 2016, with the final order's details pending negotiations.[178] In May 2016, the Danish government recommended to parliament that 27 F-35As should be procured instead of 38 Super Hornets.[179][180]
In September 2016, Boeing indicated that they would take legal action against the Danish F-35A buy, indicating that flawed data was used.[181] In March 2018, Boeing lost the case with the court stating "The court has found that the authorities' decisions on refusal of access to the documents are legal and valid."[182]
Finland
[edit]In June 2015, a working group set up by the Finnish MoD proposed starting the HX Fighter Program to replace the Finnish Air Force's current fleet of F/A-18C/D Hornets, which will reach the end of their service life by the end of the 2020s. The group recognised five potential types: Boeing F/A-18E/F Advanced Super Hornet, Dassault Rafale, Eurofighter Typhoon, Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightning II and Saab JAS 39 Gripen.[183] In May 2016, the DOD announced that Boeing (with the Super Hornet) and Lockheed Martin (with the F-35) would respond to the information request.[184] This request was sent in early 2016 with five responses received in November 2016. A call for tender will be sent in spring 2018 and the buying decision is scheduled to take place in 2021.[185]
In February 2020, three Super Hornets (a single-seat F/A-18E, a twin-seat F/A-18F and an EA-18G) arrived at the Tampere-Pirkkala Airbase in Finland for final flight evaluations.[186] The evaluations concluded on 28 February 2020.[187] The Finnish newspaper Iltalehti reported that several foreign and security policy sources had confirmed the Finnish Defense Forces recommendation of the F-35, citing its capability and expected long lifespan as key reasons.[188][189][190] Finland ordered the F-35 in February 2022.[191]
Germany
[edit]Germany requires a replacement for its aging Panavia Tornado fleet, including both Tornado IDS (interdictor/strike) and ECR (Electronic Combat/Reconnaissance) variants. Germany considered ordering the Lockheed Martin F-35, Eurofighter Typhoon, and the Boeing F/A-18E/F Super Hornet and EA-18G Growler. In April 2020, Germany's defense secretary announced a replacement plan for a split purchase of 30 Super Hornets, 15 EA-18Gs and 55 Typhoons.[192] However, the Defense Ministry states this is not finalized and it is being debated.[193] As of March 2020, the Super Hornet is not certified for the B61 nuclear bombs, but Dan Gillian, Super Hornet program head, previously stated that "We certainly think that we, working with the U.S. government, can meet the German requirements..."[194]
With increased tensions in Europe, due to the Russian invasion of Ukraine beginning 24 February 2022, Germany scrambled to accelerate defense spending priorities. Newly elected Chancellor Olaf Scholz pledged a €100 billion military upgrade, which included selecting the F-35 instead of the Super Hornet for the nuclear role and Eurofighter ECR/SEAD instead of the Growler.[195][196]
India
[edit]For India's MMRCA competition, Boeing offered a customized variant called F/A-18IN, which included Raytheon's APG-79 AESA radar.[197] In August 2008, Boeing submitted an industrial participation proposal detailing partnerships with companies in India.[198] The Indian Air Force (IAF) extensively evaluated the Super Hornet, including field trials in August 2009.[199] However, in April 2011, the IAF eliminated the F/A-18IN from the competition which was eventually won by the Dassault Rafale.[200]

In October 2016, India reportedly received three unsolicited bids, including one from Boeing for the Super Hornet, to replace its MiG-21 and MiG-27 aircraft.[201] In February 2018, the Indian Naval Air Arm was reportedly interested in the Super Hornet as the main carrier-based strike fighter of the in-development Vishal-class aircraft carrier.[202] In December 2020, Boeing announced the successful launched of the aircraft from a ski-jump, emphasizing its compatibility with the Indian Navy's STOBAR carriers.[203] In May 2022, two Super Hornets were sent to Goa to showcase compatibility with Indian aircraft carriers.[204] There are technical aspects that would make the Rafale difficult to implement for the INS Vikrant, and would favor the Super Hornet over the Rafale.[205]
The aircraft is now competing with six others in a fresh tender, referred as MMRCA 2.0, for the procurement of 114 multi-role combat aircraft for the IAF.[206]
In July 2023, the Indian Ministry of Defence revealed that the Defence Acquisition Council had granted Acceptance of Necessity for 22 Dassault Rafale M fighters and 4 Dassault Rafale DH conversion trainers for the Indian Navy.[207][208] The Rafale was chosen over the Super Hornet due to their commonality with the Rafale aircraft operated by the Indian Air Force, as well as availability to integrate Indian origin systems into the aircraft. The aircraft would complement the existing fleet of Navy Mikoyan MiG-29K aircraft, to be later joined by the Indian built Twin Engine Deck Based Fighter. The aircraft would be operated on the Indian aircraft carriers INS Vikramaditya and INS Vikrant.
Poland
[edit]During the 2010s, Poland sought to purchase 64 multirole combat aircraft from 2021 to replace the Polish Air Force's fleet of Sukhoi Su-22M4 ground attack aircraft and Mikoyan MiG-29 fighters. In November 2017, the Armament Inspectorate launched the acquisition process.[209] On 22 December 2017, five entities expressed interest in participating in the market analysis phase of the procurement, referred to as "Harpia" (harpy eagle); they included Saab (Gripen NG), Lockheed Martin (F-35), Boeing (F/A-18), Leonardo (Eurofighter Typhoon) and Fights-On Logistics (second-hand F-16).[210] On 28 May 2019, the Polish Defense Ministry formally requested to buy 32 F-35As.[211]
Switzerland
[edit]Boeing first offered the Super Hornet to the Swiss Air Force as a replacement for Swiss F-5E Tigers before withdrawing from the competition on 30 April 2008.[212] The Swiss Air Force was at one point intending to buy the rival Saab Gripen, but this was blocked by Swiss voters in 2014.[213] In March 2018, Swiss officials named contenders in its Air 2030 program: The Saab Gripen, Dassault Rafale, Eurofighter Typhoon, Boeing F/A-18E/F Super Hornet and Lockheed Martin F-35. The program has a budget of US$8 billion but includes not only combat aircraft but also ground-based air defense systems.[214][215] In October 2018, it was reported by Jane's that the Swiss Air Force may be limited to purchasing a single-engine fighter due to cost.[216] The F/A-18E/F performed demonstrations for Swiss personnel at Payerne Air Base in April 2019, which was contrasted to flights performed by other bidders.[217]
On 30 June 2021, the Swiss Federal Council proposed buying 36 F-35As to Parliament[218] at a cost of up to 6 billion Swiss francs (US$6.5 billion), citing the aircraft's cost and combat effectiveness.[219] The anti-military group GSoA intended to contest the purchase in another national referendum supported by the Green Party of Switzerland and the Social Democratic Party of Switzerland (which previously acted to block the Gripen).[220][221] In August 2022, they registered the initiative, with 120,000 people having signed in less than a year (with 100,000 required).[222] On 26 November 2021, it was announced that Armasuisse had agreed terms with the US government for 36 F-35As for CHF 6.035 billion.[223] The order was then subject to parliamentary approval and the popular initiative not proceeding or failing. A parliamentary inquiry found the purchase worrisome but legal.[224][225] The government did not wait for the popular initiative to proceed, which was legally permitted.[226] On 15 September 2022, the Swiss National council gave the Federal council permission to sign the purchase deal.[227] The deal to buy 36 F-35A was signed on 19 September 2022, with deliveries to commence in 2027 and conclude by 2030.[228][229]
Spain
[edit]By 2018, Spain sought 68-72 fighters to replace its F/A-18A/B Hornets; tender participants included the Eurofighter Typhoon, Dassault Rafale, Boeing F/A-18 E/F Advanced Super Hornet, and Lockheed F-35 Lightning II.[230] On 22 June 2022, Spain ordered 20 Tranche 4 Typhoons to replace the 20 ex-USN F/A-18s based at the Canary Islands.[231]
United States Marine Corps
[edit]The United States Marine Corps (USMC) avoided the Super Hornet program over fears that any purchased F/A-18s would be at the cost of the F-35B STOVL fighters that they intend to operate from amphibious ships. Resistance is so high that they would rather fly former Navy F/A-18Cs.[232] In 2011, the USMC agreed to eventually equip five Marine fighter-attack squadrons (VMFA) with the F-35C carrier variant to continue to augment Navy carrier air wings as they do with the F/A-18C.[233]
Others
[edit]
On 10 March 2009, Boeing offered the Super Hornet for Greece's Next-Generation Fighter Program.[234]
On 1 August 2010, The Sunday Times reported that the British government was considering canceling orders for the F-35B and buying the Super Hornet instead for its Queen Elizabeth-class aircraft carriers, claiming a saving of around £10 billion as a result. An industry source claimed that the Super Hornet could be ski jump launched without catapults.[235] In the end, the UK opted for a STOVL aircraft carrier equipped with F-35Bs.
The United Arab Emirates was reported to have asked for information on the Super Hornet in 2010.[236]
In early 2011, Bulgaria was considering the F/A-18 as a replacement for its MiG-21 fleet.[237] After initially selecting the Saab Gripen, the newly elected governing coalition restarted the program and indicated that the Super Hornet is again under consideration. The decision is expected by July 2018.[238] In December 2018, the Bulgarian Ministry of Defence selected the offer for 8 F-16V from the United States for an estimated 1.8 billion lev ($1.05 billion) as the preferred option, and recommended the government to start talks with the US.[239]
In 2012, Norway received an offer for at least one squadron of F/A-18s, noting its suitability to Northern Norwegian conditions.[240]
In 2014, Boeing worked with Korean Airlines to offer the Advanced Super Hornet to the Republic of Korea Air Force as an alternative to their KF-X fighter program. Although a fighter based on the Super Hornet would save money, downgrading the program would not give South Korean industry as much knowledge as it would from developing a new fighter.[241]
Variants
[edit]- F/A-18E
- Single seat variant
- F/A-18F
- Two-seat variant
- NEA-18G
- Two F/A-18Fs modified as prototypes of the EA-18G Growler.[242]
- EA-18G Growler
- Electronic warfare variant of the F/A-18F to replace the U.S. Navy's Northrop Grumman EA-6B Prowler.
- Advanced Super Hornet
- Variant of the F/A-18E/F Super Hornet with Conformal Fuel Tanks (CFT) and has a further reduced radar cross section (RCS), with the option of a stealthy enclosed weapons pod and built-in IRST21 sensor system. Not pursued by US Navy, but some elements such as the IRST sensor, although integrated into a fuel tank, are incorporated into the Block III. However, the Conformal Fuel Tanks and reduced RCS are still stated to be of interest to the RAAF.[243]
Operators
[edit]




- Royal Australian Air Force - 24 F/A-18F Super Hornet aircraft[citation needed]
- No. 1 Squadron (F/A-18F)
- No. 82 Wing Training Flight (F/A-18F)
- Kuwait Air Force – 22 single-seat F/A-18Es and 6 twin-seat F/A-18Fs on order[244][245]
- United States Navy
- Pacific Fleet squadrons
- VFA-2 "Bounty Hunters" (F/A-18F)
- VFA-14 "Tophatters" (F/A-18E)
- VFA-22 "Fighting Redcocks" (F/A-18F)[246]
- VFA-25 "Fist of the Fleet" (F/A-18E)
- VFA-27 "Royal Maces" (F/A-18E)
- VFA-41 "Black Aces" (F/A-18F)
- VFA-86 "Sidewinders" (F/A-18E)
- VFA-94 "Mighty Shrikes" (F/A-18E)
- VFA-102 "Diamondbacks" (F/A-18F)
- VFA-113 "Stingers" (F/A-18E)
- VFA-115 "Eagles" (F/A-18E)
- VFA-122 "Flying Eagles" (Fleet Replacement Squadron, operates F/A-18E/F)[247]
- VFA-136 "Knighthawks" (F/A-18E)
- VFA-137 "Kestrels" (F/A-18E)
- VFA-146 "Blue Diamonds" (F/A-18E)
- VFA-151 "Vigilantes" (F/A-18E)
- VFA-154 "Black Knights" (F/A-18F)
- VFA-192 "Golden Dragons" (F/A-18E)
- VFA-195 "Dambusters" (F/A-18E)
- Atlantic Fleet squadrons
- VFA-11 "Red Rippers" (F/A-18F)
- VFA-31 "Tomcatters" (F/A-18E)
- VFA-32 "Swordsmen" (F/A-18F)
- VFA-34 "Blue Blasters" (F/A-18E)[248]
- VFA-37 "Ragin Bulls" (F/A-18E)
- VFA-81 "Sunliners" (F/A-18E)
- VFA-83 "Rampagers" (F/A-18E)
- VFA-87 "Golden Warriors" (F/A-18E)
- VFA-103 "Jolly Rogers" (F/A-18F)
- VFA-105 "Gunslingers" (F/A-18E)
- VFA-106 "Gladiators" (Fleet Replacement Squadron, operates F/A-18E/F)
- VFA-131 "Wildcats" (F/A-18E)
- VFA-143 "Pukin' Dogs" (F/A-18E)
- VFA-211 "Fighting Checkmates" (F/A-18E)
- VFA-213 "Black Lions" (F/A-18F)
- Test and Evaluation squadrons
- Warfighting Development Centers
- NAWDC (Naval Aviation Warfighting Development Center, operates F/A-18E/F and other aircraft)
- Flight Demonstration squadrons
- U.S. Navy Flight Demonstration Squadron / Blue Angels (F/A-18E/F)
- Pacific Fleet squadrons
Each U.S. Navy deployable "Fleet" VFA squadron has a standard unit establishment of 12 aircraft.
Notable accidents
[edit]- On 6 April 2011, a U.S. Navy F/A-18F from VFA-122 Tactical Demonstration team crashed, killing both crew members. The crash occurred when the crew attempted to perform a loaded roll with too much speed and insufficient angle-of-attack. The loaded roll has since been removed from the Navy's F/A-18F flight demonstration routine.[249]
- On 31 July 2019, a U.S. Navy F/A-18E from VFA-151 crashed into the side of "Star Wars Canyon" in California, killing the pilot and injuring seven French civilian sightseers at the Father Crowley Vista Point 40 feet above the impact point. The crash was attributed to flying "too fast and too low with respect to the surrounding terrain". Military training within the canyon has since been suspended, with standing instructions to stay above the rim of the canyon.[250][251][252]
Specifications (F/A-18E/F)
[edit]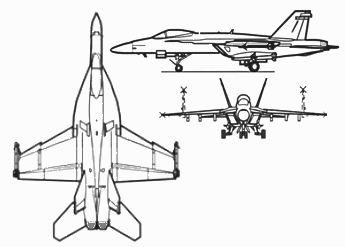


Data from U.S. Navy fact file,[3] F/A-18E/F NATOPS,[253][254][255] F/A-18E Standard Aircraft Characteristics (SAC),[256] FY 2012 Selected Acquisition Report[257]
General characteristics
- Crew: F/A-18E: 1 (pilot), F/A-18F: 2 (pilot and weapon systems officer)
- Length: 60 ft 1.25 in (18.31 m)
- Wingspan: 44 ft 8.5 in (13.62 m)
- Height: 16 ft 0 in (4.88 m)
- Wing area: 500 sq ft (46.5 m2)
- Empty weight: 32,081 lb (14,552 kg)
- Gross weight: 47,000 lb (21,320 kg) (equipped for fighter escort)
- Max takeoff weight: 66,000 lb (29,937 kg)
- Internal fuel capacity: F/A-18E: 14,700 lb (6,667 kg), F/A-18F: 13,760 lb (6,241 kg)
- External fuel capacity: Up to 4 × 480 gal (1,800 L) tanks, totaling 13,040 lb (5,914 kg), option for 2x 515 gal (1,949 L) conformal fuel tanks totaling an additional 7,000 lb (3,175 kg) on Block III[258]
- Powerplant: 2 × General Electric F414-400 turbofans, 13,000 lbf (58 kN) thrust each dry, 22,000 lbf (98 kN) with afterburner
Performance
- Maximum speed: 1,030 kn (1,190 mph, 1,915 km/h) at 40,000 ft (12,190 m)
- Maximum speed: Mach 1.6[258]
- Mach 1.06, 700 kn (806 mph; 1,296 km/h) at sea level
- Cruise speed: 482 kn (555 mph, 893 km/h) fighter escort
- Range: 1,275 nmi (1,458 mi, 2,346 km) with armament of two AIM-9s[3]
- Combat range: 444 nmi (511 mi, 822 km) combat radius for interdiction mission with 2 × 480-gallon drop tanks[257]
- Ferry range: 1,800 nmi (2,070 mi, 3,330 km)
- Service ceiling: 52,300 ft (15,940 m)
- Rate of climb: 44,882 ft/min (228 m/s)
- Wing loading: 94.0 lb/sq ft (459 kg/m2) or 127.0 lb/sq ft (620 kg/m2) at max takeoff weight
- Thrust/weight: 0.93[260]
- Design load factor: 7.5 g[257]
Armament
- Guns: 1× 20 mm (0.787 in) M61A2 Vulcan, 412 rounds[255]
- Hardpoints: 11 (2× wingtips, 6× under-wing, and 3× under-fuselage) with a capacity of Max payload: 17,750 lb (8,050 kg). Carrier bringback payload: F/A-18E: 9,900 lb (4,491 kg), F/A-18F: 9,000 lb (4,082 kg)[258], with provisions to carry combinations of:
- Missiles:
- Air-to-air missiles
- 4× AIM-7 Sparrow
- 4× AIM-9 Sidewinder
- 12× AIM-120 AMRAAM
- 12× AIM-260 JATM (to be integrated)
- 2× AIM-174B[261][N 3][262]
- Air-to-surface missiles
- 6× AGM-65E/F Maverick
- 4× AGM-84H/K SLAM-ER
- 6× AGM-88 HARM
- 4x AGM-158 JASSM
- 4× AGM-154 Joint Standoff Weapon (JSOW) - glide bomb
- 4× AGM-84 Harpoon
- 4× AGM-158C LRASM
- Joint Strike Missile (JSM) (to be integrated)
- Air-to-air missiles
- Bombs:
- JDAM bombs (up to 10× GBU-32/35/38/54 or 4× GBU-31)
- Paveway series of laser-guided bombs
- Mk 80 series unguided bombs
- CBU-78 Gator mine system[citation needed]
- Mk 20 Rockeye II cluster bomb[citation needed]
- Mk-62/63/65 Quick Strike Naval mine
- Other:
- SUU-42A/A Flares/infrared decoy dispenser pod and chaff pod
- AN/ALE-50 towed decoy system pod
- AN/ASQ-228 ATFLIR or AN/AAQ-28(V) Litening[263] targeting pods
- up to 4× 480 US gal (1,800 L; 400 imp gal) drop tanks and 1× A/A42R-1 Aerial Refueling Store pod for aerial refueling.
- 12× ADM-141C TALD decoys
- AWW-13 Advanced data link pod
- Missiles:
Avionics
- Hughes APG-73 or Raytheon APG-79 radar
- Northrop Grumman/ITT ALQ-165 self-protection jammer system or L3Harris AN/ALQ-214 integrated defensive electronic countermeasures system
- Raytheon AN/ALE-50 or BAE Systems AN/ALE-55 towed decoy
- Raytheon AN/ALR-67(V)3 radar warning receiver
- Lockheed Martin AN/ASG-34(V) infrared search and track (mounted on centerline external tank)
- MIDS LVT or MIDS JTRS datalink transceiver
See also
[edit]Related development
Aircraft of comparable role, configuration, and era
Related lists
- List of fighter aircraft
- List of active United States military aircraft
- List of United States military aerial refueling aircraft
References
[edit]Notes
[edit]Citations
[edit]- ^ "Navy takes delivery of final Block II Super Hornet, looks ahead to Block III". Naval Air Systems Command, U.S. Navy, 23 April 2020.
- ^ a b c "Govt to keep Super Hornets." Archived 6 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine The Age, 17 March 2008.
- ^ a b c d e "F/A-18 fact file." Archived 11 January 2014 at the Wayback Machine U.S. Navy, 13 October 2006. Retrieved: 25 July 2011.
- ^ Baugher, Joe (20 July 2009). "Northrop YF-17 Cobra". joebaugher.com. Archived from the original on 7 November 2014. Retrieved 27 September 2014.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Jenkins, Dennis R. F/A-18 Hornet: A Navy Success Story. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2000. ISBN 0-07-134696-1.
- ^ a b c "F/A-18E/F Super Hornet." Archived 11 April 2007 at the Wayback Machine Boeing. Retrieved: 25 July 2011.
- ^ Donald 2004, p. 45.
- ^ Aronstein, David; Hirschberg, Michael (1998). Advanced Tactical Fighter to F-22 Raptor: Origins of the 21st Century Air Dominance Fighter. Arlington, Virginia: American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics. p. 240. ISBN 978-1-56347-282-4.
- ^ Elward 2001, p. 73.
- ^ a b Rogoway, Tyler (13 May 2014). "TOP GUN Day Special: The Super Tomcat That Was Never Built". jalopnik.com. Archived from the original on 18 November 2016. Retrieved 12 November 2016.
- ^ "F-14 Tomcat - Military Aircraft". Archived from the original on 2 February 2016. Retrieved 14 February 2016.
- ^ Donald, David. "Northrop Grumman F-14 Tomcat, U.S. Navy today". Warplanes of the Fleet. London: AIRtime Publishing Inc, 2004. ISBN 1-880588-81-1.
- ^ "FUTURE OF NAVAL AVIATION -- HON.RANDY'DUKE'CUNNINGHAM (Extension of Remarks - May 07, 1991)". Archived from the original on 8 May 2016. Retrieved 9 February 2016.
- ^ Donald 2004, pp. 13, 15.
- ^ Young, James; Anderson, Ronald; Yurkovich, Rudolph (1998). "A description of the F/A-18E/F design and design process". 7th AIAA/USAF/NASA/ISSMO Symposium on Multidisciplinary Analysis and Optimization. Multidisciplinary Analysis Optimization Conferences. American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics. doi:10.2514/6.1998-4701.
- ^ Younossi, Obaid; Stem, David E.; Lorell, Mark A.; Lussier, Frances M. (2005). Lessons Learned from the F/A–22 and F/A–18E/F Development Programs (Report). RAND Corporation. Archived from the original on 25 April 2011. Retrieved 27 August 2011.
- ^ Kopp, Dr Carlo (June 2001). "Flying the F/A-18F Super Hornet". Australian Aviation. 2001 (May). Archived from the original on 27 September 2014. Retrieved 27 September 2014.
- ^ Frost, Patricia (28 March 1997). "F/A-18E/F Super Hornet Approved For Low-Rate Production". Boeing.com. Archived from the original on 6 February 2010. Retrieved 16 August 2010.
- ^ Frost, Patricia (22 September 1997). "F/A-18E/F Super Hornet Enters Production at Boeing". Boeing. Archived from the original on 6 February 2010. Retrieved 16 August 2010.
- ^ "Operational and Test Evaluation of F/A-18E/F and F-22 review to Senate Armed Services Committee" (PDF). Armed-services.senate.gov. 22 March 2000. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 November 2012. Retrieved 25 July 2011.
- ^ Nathman, John, Rear Admiral U.S. Navy. "DoD Special Briefing on "Super Hornet" Operation Evaluation Results." Archived 8 June 2011 at the Wayback Machine Defenselink.mil, 15 September 2000. Retrieved: 8 July 2011.
- ^ "The F/A-18E/F Super Hornet: Tomorrow's Air Power Today". National Defense Industrial Association. 4 July 2008. Archived from the original on 28 May 2008.
- ^ Trimble, Stephen (23 July 2007). "US Navy Super Hornet deal could cut JSF numbers". Flight Global. Archived from the original on 6 July 2008.
- ^ a b "Boeing F/A-18E/F Super Hornet a Finalist in Brazil Fighter Aircraft Competition" (Press release). Boeing. 1 October 2008. Archived from the original on 22 February 2014.
- ^ "Navy F/A-18E/F and EA-18G Aircraft Procurement and Strike Fighter Shortfall: Background and Issues for Congress". opencrs.com. 29 May 2009. Archived from the original on 7 July 2009. Retrieved 16 August 2010.
- ^ "DoD News Briefing With Secretary Gates From The Pentagon". United States Department of Defense. 6 April 2009. Archived from the original on 6 August 2011. Retrieved 9 September 2011.
- ^ Tilghman, Andrew (8 June 2006). "Gates: Fighter gap ignores real-world demand". Navy Times. Archived from the original on 7 September 2012. Retrieved 16 August 2010.
- ^ Shalal-Esa, Andrea. "US defense compromise authorizes F/A-18 multiyear deal". Forbes. Retrieved 16 August 2010. [dead link]
- ^ Tilghman, Andrew (25 June 2009). "Bill would give go-ahead to buy Super Hornets". Navy Times. Archived from the original on 4 September 2012. Retrieved 16 August 2010.
- ^ Leiser, Ken (29 September 2010). "Boeing lands $5.3 billion fighter jet contract with Navy". St. Louis Post-Dispatch. Archived from the original on 30 September 2010. Retrieved 29 September 2010.
- ^ Wolfe, Frank (11 February 2020). "Boeing Super Hornets Receiving Block III Avionics Upgrades". Aviation today. Retrieved 19 May 2020.
- ^ Cameron, Doug. "Boeing to End Production of Super Hornet Combat Jet, Co-Star of 'Top Gun: Maverick'". WSJ. Retrieved 24 February 2023.
- ^ Finnerty, Ryan (20 March 2024). "Boeing extends Super Hornet production to 2027 with final new-build order from USA". Flight Global. Retrieved 19 April 2024.
- ^ a b c Ozburn, Marguerite. "F/A-18E/F Block II upgrades add to Super Hornet's potent arsenal." Archived 12 October 2007 at the Wayback Machine Boeing Frontiers, June 2005. Retrieved: 25 July 2011.
- ^ a b c Fulghum, David A. (25 February 2007). "Navy Details New Super Hornet Capabilities". Aviation Week and Space Technology. Archived from the original on 23 February 2012. Retrieved 31 December 2023.
- ^ Reed, John. "Boeing: F-35 hasn’t yet won in Japan." Archived 9 January 2012 at the Wayback Machine DoD Buzz, 16 December 2011.
- ^ Jennings, Faith. "Raytheon to Provide Revolutionary AESA Capabilities to 135 F/A-18s." Archived 14 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine Raytheon, 23 January 2008. Retrieved: 25 July 2011.
- ^ "Block III Super Hornet". Boeing. 8 May 2020.
- ^ Fulghum, David. A. "Boeing Plans Sixth Generation Fighter With Block 3 Super Hornet" (subscription required). Aviation Week, 30 January 2008. Retrieved: 17 February 2008.
- ^ Eckstein, Megan (27 September 2021). "Boeing delivers first Block III Super Hornets to the US Navy". Defense News.
- ^ Tournade, Sara. "Boeing well positioned for future strike-fighter market." Archived 26 January 2012 at the Wayback Machine Boeing, 21 June 2011. Retrieved: 18 December 2011.
- ^ Minnick, Wendell. "Boeing Unveils New Hornet Options at Aero India". Defense News, 8 February 2011.
- ^ Nativi, Andy. "Boeing Reveals Details Of International F-18." [dead link] Aviation Week, 4 November 2011.
- ^ Barrie, Douglas, Amy Butler and Robert Wall. "Manufacturers Vie To Close Fighter Gap." [dead link] Aviation Week, 30 July 2010. Retrieved: 25 July 2011.
- ^ "Testing the next-generation Super Hornet." Archived 15 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine Flight International, 12 July 2011. Retrieved: 25 July 2011.
- ^ "Boeing Receives US Navy Contract to Develop New Mission Computer for Super Hornet and Growler." Archived 18 November 2011 at the Wayback Machine Space Media Network, 15 November 2011.
- ^ Frost, Patricia. "Boeing Selects Supplier for Super Hornet Block II Infrared Search and Track Capability." Archived 23 September 2013 at the Wayback Machine Boeing, 2 July 2007.
- ^ a b Greenert, Admiral Jonathan (18 September 2013). "Statement Before The House Armed Services Committee On Planning For Sequestration In FY 2014 And Perspectives Of The Military Services On The Strategic Choices And Management Review" (PDF). US House of Representatives. Archived (PDF) from the original on 23 September 2013. Retrieved 21 September 2013.
- ^ Kelly, Heather (18 May 2009). "Lockheed Martin Awarded Technology Development Contract for F/A-18E/F Infrared Search and Track Program". Lockheed Martin Press Release. Archived from the original on 23 May 2009.
- ^ Hilliard, Melissa (22 November 2011). "Lockheed Martin Awarded U.S. Navy F/A-18 E/F IRST Sensor System EMD Contract". Archived from the original on 25 November 2011.
- ^ a b "F/A-18's Infrared Search And Track System Plagued By Delays". The War Zone. 9 June 2023.
- ^ Andrea Shalal-Esa. "Boeing aims to keep building F/A-18 jets through 2020". Fox Business. Archived from the original on 2 April 2015. Retrieved 1 April 2015.
- ^ "Boeing: Advanced Super Hornet makes its debut". Archived from the original on 31 August 2013.
- ^ Boeing to demo Super Hornet enhancements in summer Archived 10 September 2013 at the Wayback Machine Flightglobal.com, 9 April 2013
- ^ "Boeing Pushing Airframe Envelope". Defense News. Archived from the original on 13 September 2013. Retrieved 1 April 2015.
- ^ "Boeing shows off advanced Super Hornet demonstrator." Archived 3 September 2013 at the Wayback Machine Flight International, 28 August 2013.
- ^ "Advanced Super Hornet Demonstrates Significant Stealth, Range Improvements." Archived 1 September 2013 at the Wayback Machine Deagel, 28 August 2013.
- ^ "Navy pleased with "Advanced" Super Hornet tests, wants more Growlers." Archived 8 April 2014 at the Wayback Machine Flight International, 7 April 2014.
- ^ Insinna, Valerie (8 April 2018). "How stealthy is Boeing's new Super Hornet?". Defense News.
- ^ Norris, Guy. "Future Options: Conformal fuel tank attracts Navy interest as part of possible Super Hornet upgrade"[permanent dead link](subscription required). Aviation Week and Space Technology, 16 December 2013, pp. 28–29.
- ^ US Navy may add conformal fuel tanks to F/A-18E/F Super Hornet fleet Archived 10 September 2013 at the Wayback Machine Flightglobal.com, 20 March 2013.
- ^ "The Navy suspends plans to give its Super Hornet a conformal fuel tank". 26 August 2021. Archived from the original on 15 January 2022. Retrieved 15 January 2022.
- ^ Norris, Guy. "GE Eyes More Powerful Engine For Super Hornets, Growlers." [dead link] Aviation Week, 14 May 2009. Retrieved: 25 July 2011.
- ^ Trimble, Stephen. "Boeing's Super Hornet seeks export sale to launch 20% thrust upgrade." Archived 15 May 2009 at the Wayback Machine Flight International, 12 May 2009.
- ^ "Boeing plots hybrid Super Hornet/Growler future." Archived 29 June 2014 at the Wayback Machine Flight International, 25 June 2014.
- ^ Kress, Bob; Gilchrist, Rear Admiral USN ret. Paul (February 2002). "F-14D Tomcat vs. F/18 E/F Super Hornet". Flight Journal Magazine. Archived from the original on 28 September 2011.
- ^ "The F-18 Super Hornet is also called the "Rhino" because of a rhino-like protrusion on the front part of the aircraft's radome". Defense Logistics Agency. 14 June 2005.
- ^ a b "Boeing Super Hornet Demonstrates Aerial Refueling Capability". Boeing Global Strike Systems. 14 April 1999. Archived from the original on 4 November 2011. Retrieved 25 July 2011.
- ^ Donald 2004, p. 76.
- ^ Majumdar, Dave (1 April 2014). "UCLASS Could Be Used as Tanker for Carrier Air Wing". news.usni.org. U.S. NAVAL INSTITUTE. Archived from the original on 4 April 2014. Retrieved 3 April 2014.
- ^ "DGC International".
- ^ a b Donald 2004, pp. 49–52.
- ^ "F/A-18E/F Super Hornet – maritime strike attack aircraft." Archived 11 August 2011 at the Wayback Machine naval-technology.com. Retrieved: 9 September 2011.
- ^ a b c Elward 2001, p. 77.
- ^ Peterson, Donald (June 2002). "Ready On Arrival: Super Hornet Joins The Fleet: An Evolutionary Design Delivers Revolutionary Capabilities". Sea Power. Navy League. Archived from the original on 20 June 2002.
- ^ Elward 2001, pp. 74–75.
- ^ a b "F/A-18E/F Super Hornet." Archived 16 January 2007 at the Wayback Machine Boeing. Retrieved: 16 August 2010.
- ^ Niewoehner, Robert "Knockers" (20 February 2023). "Super Hornet Chief Test Pilot". Test Pilot Series (Interview). Interviewed by Sinclair, Brian "Sunshine". Authentic Media.
- ^ a b Gaddis, Capt. "BD". "F/A-18 & EF-18G Program brief." Archived 28 May 2008 at the Wayback Machine U.S. Navy, 24 April 2007.
- ^ "F/A-18-E/F Super Hornet... Leading Naval Aviation into the 21st Century." Archived 26 February 2011 at the Wayback Machine U.S. Navy, 17 August 2009.
- ^ a b Donald 2004, pp. 50–51, 56.
- ^ "USN looking at adding conformal fuel tanks on F/A-18E/F--also a look at Super Hornet RCS reduction measures". The DEW Line. Archived from the original on 8 June 2013. Retrieved 1 April 2015.
- ^ Winchester 2006, p. 166.
- ^ "Boeing F/A-18 Super Hornet". airframer.com. Archived from the original on 17 September 2011. Retrieved 12 February 2011.
- ^ "New APG-79 AESA Radars for Super Hornets." Archived 7 June 2011 at the Wayback Machine Defense Industry Daily, 26 April 2005. Retrieved: 8 July 2011.
- ^ "New U.S. Navy Radar Detects Cruise Missiles." Aviation Week and Space Technology, 30 April 2007.
- ^ Cormier, Nicolette (8 July 2002). "F/A-18 AESA – New Technology Revolutionizes Radar Benefits". U.S. Navy. Archived from the original on 13 February 2015. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- ^ Boeing (8 January 2007). "Boeing F/A-18E/F Block 2 Super Hornets Flying at Naval Air Station Oceana". Boeing.com. Archived from the original on 17 January 2007.
- ^ "Boeing Dual-Cockpit Cueing System Introduced to U.S. Navy Squadron." Archived 21 December 2007 at the Wayback Machine defense-aerospace.com. Retrieved 16 August 2010.
- ^ Clemons, John. "Raytheon Awarded Navy Contract to Increase SHARP System Capability." Archived 14 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine Raytheon, 4 October 2006.
- ^ Rosenberg-Macaulay, Barry. "MIDS JTRS systems poised to bring IP networking to the aerial tier." Archived 15 December 2010 at the Wayback Machine defensesystems.com, 2011. Retrieved: 12 February 2011.
- ^ "JTRS Update: MIDS Blazes JTRS Trail". Military Information Technology. 14 (8). September 2010. ISSN 1097-1041. Archived from the original on 14 July 2011. Retrieved 12 February 2011.
- ^ Ben Werner (4 April 2019). "Navy's Next-Generation Fighter Analysis Due Out this Summer". USNI News. Archived from the original on 7 June 2019. Retrieved 7 June 2019.
- ^ Naval Aviation News March–April 1999, p. 30 "fleet service in January 1999"[full citation needed]
- ^ "Navy's Last F-18 Hornet Squadron Sundowns Ahead of Transition to Super Hornet". USNI News. 4 February 2019.
- ^ "Strikes Continue: ISAF Air Component Commander Visits Big E." (Press release). United States Navy. 9 November 2006. Archived from the original on 7 August 2011. Retrieved 9 September 2011.
- ^ Svan, Jennifer H. (13 October 2006). "USS Enterprise aircraft deliver lethal sting of bombs to enemy in Afghanistan". Stars and Stripes. Archived from the original on 29 June 2011.
- ^ Moore, Shannon (22 May 2007). "CVW-7 Sailors Complete an Eight-Month Deployment" (Press release). United States Navy. Archived from the original on 29 March 2012. Retrieved 16 August 2010.
- ^ Cenciotti, David (20 January 2014). "U.S. F/A-18E Hornet operates from French Aircraft Carrier". The Aviationist. Archived from the original on 14 May 2015. Retrieved 8 May 2015.
- ^ U.S. fighters pound militants in northern Iraq Archived 8 August 2014 at the Wayback Machine - Militarytimes.com, 7 August 2014
- ^ USN carries out air strike on Iraqi militants Archived 9 August 2014 at the Wayback Machine - Flightglobal.com, 8 August 2014
- ^ Naval Power Bolsters U.S. Airstrikes in Iraq Archived 12 August 2014 at the Wayback Machine - Defensetech.org, 8 August 2014
- ^ "US F/A-18E Shoots Down Syrian Su-22 in Air-to-Air Kill" Archived 18 June 2017 at the Wayback Machine. Military.com, 18 June 2017.
- ^ Report: Navy Pilot Breaks Silence About Shooting Down Syrian Fighter Archived 1 August 2017 at the Wayback Machine - Military.com, 31 July 2017
- ^ Garrett Reim (15 August 2018). "Boeing to convert F/A-18 E/Fs into Blue Angels". flightglobal.com. Archived from the original on 16 August 2018. Retrieved 16 August 2018.
- ^ LaGrone, Sam (26 December 2023). "U.S Destroyer, Super Hornets Splash Red Sea Attack Drones and Missiles". USNI News. Retrieved 31 December 2023.
- ^ U.S. Hits Houthi Targets in Yemen with Strike Fighters, Warships and Submarines. USNI News. 11 January 2024.
- ^ Ike’s Carrier Air Wing 3, USS Gravely, USS Philippine Sea and USS Mason Struck Houthi Targets. USNI News. 12 January 2024.
- ^ US, UK Strike Houthis in Yemen Following Ship Attacks. Air & Space Forces Magazine. 11 January 2024.
- ^ "Super Hornet Acquisition Contract Signed." defence.gov.au, 5 March 2007. Retrieved: 16 August 2010.
- ^ Baker, Richard. "The Hornet's nest." Archived 12 July 2007 at the Wayback Machine The Age, 9 July 2007.
- ^ "Australia to Acquire 24 F/A-18F Super Hornets". minister.defence.gov.au. 6 March 2007. Archived from the original on 12 March 2011. Retrieved 16 August 2010.
- ^ "Acceptance for Super Hornets A44-202 and A44-204."Archived 2 August 2012 at archive.today Defence.gov.au, 26 February 2010. Retrieved: 16 June 2011.
- ^ a b "The 7.30 Report: Nelson stands by fighter jet decision." Archived 12 October 2007 at the Wayback Machine Australian Broadcasting Corporation (ABC), 15 March 2007.
- ^ Criss, Peter. "There is nothing super about this Hornet." Archived 12 October 2007 at the Wayback Machine The Sydney Morning Herald, 15 March 2007. Retrieved: 9 May 2007.
- ^ Allard, Tom. "Axe set to fall on Nelson's fighters." Archived 2 January 2008 at the Wayback Machine The Sydney Morning Herald, 31 December 2007.
- ^ "Government clears Super Hornets deal." Archived 3 May 2014 at the Wayback Machine The Age, 17 March 2008.
- ^ Dunlop, Tim. "Super Hornets are go." Archived 1 December 2008 at the Wayback Machine news.com.au, 18 March 2008.
- ^ "Australia – F/A-18E/F Super Hornet Aircraft" (PDF). U.S. Defense Security Cooperation Agency. 6 February 2007. Archived from the original (PDF) on 26 February 2009.
- ^ Smith, Jack. "Super Hornets wired for future upgrades." Archived 23 March 2012 at the Wayback Machine Department of Defence, 27 February 2009. Retrieved: 9 September 2011.
- ^ Carder, Phillip. "Boeing F/A-18F Super Hornet for Australia Takes Flight." Archived 25 July 2011 at the Wayback Machine Boeing, 21 July 2009.
- ^ "Super Hornets arrive in south-east Queensland." Archived 13 November 2012 at the Wayback Machine ABC News, 26 March 2010. Retrieved: 15 July 2011.
- ^ Hurst, Daniel. "Pilots buzzing as Super Hornets arrive." Archived 9 July 2010 at the Wayback Machine The Brisbane Times, 6 July 2010.
- ^ Waldron, Greg. "Australia’s first F/A-18F squadron declared operational." Archived 12 December 2010 at the Wayback Machine Flight International, 9 December 2010.
- ^ Dodd, Mark (15 August 2008). "RAAF likes the sound of the Growler". The Australian. Archived from the original on 17 August 2008.
- ^ "Joint Media Release: Australia’s future Air Combat Capability." Archived 12 March 2013 at the Wayback Machine Minister for Defence and Minister for Defence Materiel (Australian Government Department of Defence), 13 December 2012.
- ^ Taylor, Charles and Paul Ebner. "F/A-18E/F Super Hornet and EA-18G Growler Aircraft". Archived 14 July 2015 at the Wayback Machine Defense Security Cooperation Agency, 28 February 2013.
- ^ "Australia plans to buy 12 EA-18G Growlers." Archived 21 October 2013 at the Wayback Machine Washingtonexaminer.com, 3 May 2013.
- ^ "Boeing: Boeing Australia — RAAF EA-18G Growler Rollout". Boeing. Archived from the original on 12 November 2016. Retrieved 12 November 2016.
- ^ "Boeing Unveils First Royal Australian Air Force Growler". News Releases/Statements. Boeing. Archived from the original on 12 November 2016. Retrieved 12 November 2016.
- ^ "Australian fighter jets and air force personnel arrive in Middle East". The Guardian. Australian Associated Press. 24 September 2022. Retrieved 15 August 2022.
- ^ "Australian Super Hornet fighter jets complete first armed mission over Iraq". ABC News (Australia). 5 October 2014. Archived from the original on 6 October 2014.
- ^ "RAAF conducts first Iraq combat mission". ABC News (Australia). Archived from the original on 6 October 2014. Retrieved 6 October 2014.
- ^ Australia launches first airstrike in Iraq Archived 9 October 2014 at the Wayback Machine - Militarytimes.com, 8 October 2014
- ^ "6 Squadron Completes Final Super Hornet Flight". australianaviation.com.au. 28 November 2016.
- ^ "Pilots forced to EJECT as military jet emergency unfolds at RAAF base Amberley". 7news.com.au. 8 December 2020. Retrieved 11 December 2020.
- ^ "Defence grounds Super Hornet, Growler warplanes after aborted take-off at Amberley RAAF base". abc.net.au. 9 December 2020. Retrieved 11 December 2020.
- ^ Greene, Andy (7 June 2022). "Investigators find pilot error responsible for aborted Super Hornet takeoff outside Brisbane". ABC News (Australia). Archived from the original on 11 June 2022.
- ^ "Kuwait to order Boeing F/A-18 fighters worth $3 bn". AFP via Business Insider. 7 May 2015. Archived from the original on 21 June 2015. Retrieved 21 June 2015.
- ^ Kuwait, Italy Discuss Eurofighter Buy. Defense News,
- ^ "Kuwait Opts For Eurofighter Typhoon". Aviation Week. 11 September 2015. Archived from the original on 28 September 2015. Retrieved 13 September 2015.
- ^ "Kuwait, Qatar Deals Move Forward, Likely Putting Boeing Fighter Jet Production Into the 2020s". Defense News, 17 November 2016.
- ^ "The Government of Kuwait – F/A-18E/F Super Hornet Aircraft with Support | the Official Home of the Defense Security Cooperation Agency". Archived from the original on 14 November 2017. Retrieved 22 November 2017.
- ^ Werner, Ben (28 June 2019). "Boeing Awarded $1.5B Contract for 28 Kuwait Super Hornets". USNI News. Archived from the original on 27 June 2019. Retrieved 27 June 2019.
- ^ Gareth, Jennings (15 January 2021). "Covid-19 impacts Super Hornet timeline for Kuwait". Janes.
- ^ "Demise of Super Hornet May Not Be Greatly Exaggerated After All". Defense-aerospace.com. Retrieved 3 August 2022.
- ^ "Super Hornets, Awacs may feature in RMAF modernisation plans" Archived 6 December 2008 at the Wayback Machine. Utusan Malaysia, 16 April 2007. Retrieved: 5 September 2008.
- ^ John Gilbert. "Three fighter jet makers to submit leasing bids". themalaysianreserve.com. Archived from the original on 19 August 2014. Retrieved 1 April 2015.
- ^ "Wordt dit de vervanger van de Belgische F-16's?" De Morgen, 12 March 2014. Retrieved: 13 March 2014.
- ^ Maass, Ryan (20 April 2017). "Boeing pulls out of 'unfair' Belgian fighter replacement bid". United Press International. Archived from the original on 19 December 2017. Retrieved 19 December 2017.
- ^ Giangreco, Leigh (19 April 2017). "Boeing pulls out of Belgian fighter competition". Flight Global. Washington, DC. Archived from the original on 19 December 2017. Retrieved 19 December 2017.
- ^ Emmott, Robin (25 October 2018). "Belgium picks Lockheed's F-35 over Eurofighter on price". Reuters. Brussels. Archived from the original on 25 October 2018. Retrieved 26 October 2018.
- ^ Insinna, Valerie (25 October 2018). "F-35 officially wins Belgian fighter contest". Defense News. Washington. Archived from the original on 25 October 2018. Retrieved 26 October 2018.
- ^ Trimble, Stephen. "Brazil names three finalists for F-X2 contract, rejects three others" Archived 1 February 2009 at the Wayback Machine. Flight International, 6 October 2008.
- ^ Mallén, Patricia Rey (16 December 2013). "Brazil Says No To $4B Fighter Jet Deal With France's Dassault; Not A Victory Yet For Boeing, Saab". International Business Times. Archived from the original on 10 February 2015. Retrieved 28 September 2014.
- ^ Osborne, Anthony (18 December 2013). "Brazil Selects Gripen For F-X2 Requirement". Aviation Week. Archived from the original on 19 December 2013. Retrieved 19 December 2013.
- ^ Rogoway, Tyler (12 June 2014). "The Right Fighter For Canada Is The Super Hornet, Not The F-35". jalopnik.com. Archived from the original on 14 November 2016. Retrieved 12 November 2016.
- ^ "Aviation companies decry F-35 purchase". CBC News. 5 November 2010. Archived from the original on 6 November 2010.
- ^ Campion-Smith, Bruce. "Ottawa to overhaul purchase of F-35 fighter jets in wake of Auditor General’s report". Toronto Star, 2 April 2012.
- ^ "Competition heats up as Ottawa reviews options to procure costly F-35 fighter jets" Archived 9 September 2013 at the Wayback Machine. Hilltimes.com, 5 September 2013
- ^ Berthiaume, Lee; Ivison, John. "Liberals planning to buy Super Hornet fighter jets before making final decision on F-35s, sources say" Archived 5 June 2016 at archive.today. National Post, 5 June 2016.
- ^ "Liberals to buy 18 Boeing Super Hornet fighter jets to fill 'capability gap'". Canadian Broadcasting Corporation. 22 November 2016. Archived from the original on 23 November 2016.
- ^ a b "U.S. State Dept. approves Canadian purchase of Super Hornet fighter jets - CBC News". Archived from the original on 21 September 2017. Retrieved 27 September 2017.
- ^ "Fallon warns Boeing over defence contracts". BBC News. 27 September 2017. Archived from the original on 11 August 2018. Retrieved 21 July 2018 – via bbc.com.
- ^ "Bombardier hit with 219% duty on sale of jets to Delta Air Lines". The Toronto Star. 26 September 2017. Archived from the original on 28 September 2017. Retrieved 27 September 2017.
- ^ "100- to 150-Seat Large Civil Aircraft from Canada Do Not Injure U.S. Industry, Says USITC" (Press release). United States International Trade Commission. 26 January 2018.
- ^ "Boeing says dispute with Bombardier still on despite Liberal plan to buy used jets". 8 December 2017. Archived from the original on 10 December 2017. Retrieved 9 December 2017.
- ^ "News Releases/Statements". Archived from the original on 9 December 2017. Retrieved 9 December 2017.
- ^ "Boeing acknowledges Super Hornet sale to Canada effectively dead". Archived from the original on 10 December 2017. Retrieved 9 December 2017.
- ^ Ljunggren, David (25 November 2021). "Canada tells Boeing its bid for C$19 bln fighter jet contract falls short". Reuters. Archived from the original on 26 November 2021.
- ^ "Government of Canada announces key milestone in process to replace Canada's fighter jets". December 2021. Archived from the original on 5 December 2021.
- ^ GDC (27 November 2021). "Boeing's Super Hornet Does Not Meet Canada's FFCP Requirement: Report". Global Defense Corp. Retrieved 29 November 2021.
- ^ Warwick, Graham. "Boeing Submits Danish Super Hornet Proposal". Aviation Week, 28 August 2008. Archived 7 March 2012 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Brett, Mary Ann and Philip Carder. "Boeing, US Navy Offer Super Hornet for Denmark Fighter Competition" Archived 22 February 2014 at the Wayback Machine Boeing, 27 August 2008.
- ^ "Denmark Prioritizes Jobs in New Fighter Competition". Defense News. Archived from the original on 18 January 2014. Retrieved 1 April 2015.
- ^ defense-aerospace.com Denmark Starts Fighter Evaluation Process to Replace F-16 Archived 19 April 2014 at the Wayback Machine 12 April 2014
- ^ "Denmark Further Postpones Fighter Selection Until 2016". Defense News. 5 December 2015. Retrieved 18 April 2016.
- ^ "Danish Government Recommends Buying 27 F-35s". defensenews.com. 12 May 2016. Archived from the original on 27 May 2016.
- ^ "Status on Danish fighter competition: Government recommends 27 F-35A – no decision yet". 16 May 2016. Archived from the original on 21 May 2016. Retrieved 23 May 2016.
- ^ "A cautionary tale for Canada? Boeing preps legal challenge after Denmark rejects Super Hornet for F-35". nationalpost.com. Retrieved 17 September 2016.
- ^ Jensen, Teis; Jacobsen, Stine; Merriman, Jane (23 March 2018). "Boeing loses case against Denmark over fighter jet deal". Reuters. Copenhagen. Archived from the original on 2 June 2019.
- ^ "Working group proposes multi-role fighters to replace F/A-18 aircraft". 11 June 2015. Archived from the original on 18 June 2015.
- ^ "Yhdysvallat tarjoaa kahta konetyyppiä Hornetin seuraajaksi". 2 May 2016. Archived from the original on 3 May 2016. Retrieved 3 May 2016.
- ^ "The Finnish Defence Forces' Logistics Command received responses concerning the replacement of the Hornet aircraft" (press release). FI: Ministry of Defence. 22 November 2016. Archived from the original on 13 March 2017. Retrieved 15 March 2017.
- ^ "U.S., Boeing send 3 Super Hornets to Finland for aircraft upgrade". UPI. Retrieved 22 April 2020.
- ^ "HX Challenge completed successfully". The Finnish Air Force (ilmavoimat.fi). 28 February 2020. Retrieved 22 April 2020.
- ^ "IL:n tiedot: Puolustusvoimat esittää yhdysvaltalaista F-35:ttä Suomen uudeksi hävittäjäksi".
- ^ "Finland Chooses F-35 as Its Next Fighter: Report". 6 December 2021.
- ^ "F-35 Selected by the Finnish Defense Forces to Replace F/A-18 Hornets According to Local Media". 6 December 2021.
- ^ Jennings, Gareth (11 February 2022). "Finland signs for F-35s". Janes. Retrieved 21 April 2022.
- ^ Perry, Dominic. "Germany picks Super Hornet and more Eurofighters for Tornado replacement". Flight Global, 21 April 2020.
- ^ "Germany won't be buying US planes to replace aging Tornados before 2022, official says". Stars and Stripes.
- ^ Trevithick, Joseph (3 April 2019). "Here's Where Boeing Aims To Take The Super Hornet In The Decades To Come". The War Zone. Archived from the original on 10 July 2019.
- ^ "Germany to buy 35 Lockheed F-35 fighter jets from U.S. amid Ukraine crisis". Reuters. 14 March 2022. Retrieved 21 April 2022.
- ^ Huguelet, Austin (14 March 2022). "Germany to buy F-35s, upgrade Eurofighters in blow to Boeing". St. Louis Post-Dispatch. Retrieved 21 April 2022.
- ^ Nelson, Brian; Sharma, Kapil (24 April 2008). "Boeing Delivers Proposal to Equip Indian Air Force with Super Hornet Fighters". Boeing. Archived from the original on 28 April 2008. Retrieved 29 April 2008.
- ^ Nelson, Brian; Rangachari, Swati (4 August 2008). "Boeing Submits Combat Aircraft Industrial-Participation Proposal to Indian Government". Boeing. Archived from the original on 8 September 2008.
- ^ "F-18 comes in first, trials begin" . Times of India, 18 August 2009. Retrieved: 16 August 2010.
- ^ Bajaj, Vikas. "U.S. Loses Bids to Supply Jets to India" Archived 28 December 2016 at the Wayback Machine. The New York Times, 28 April 2011. Retrieved: 11 May 2011.
- ^ Bedi, Rahul (14 October 2016). "India renews search for MiG replacement". IHS Janes. Archived from the original on 16 October 2016.
- ^ "Boeing in Talks With Indian Navy to Sell F/A-18 Fighter Jets". BloombergQuint. 5 February 2018. Archived from the original on 7 February 2019. Retrieved 5 February 2019.
- ^ "F/A-18 operation on Indian carriers successfully demonstrated: Boeing". The Hindu. 21 December 2021.
- ^ Peri, Dinakar (23 May 2022). "Two F-18 Super Hornet jets in Goa to showcase compatibility with Indian aircraft carriers". The Hindu.
- ^ "Rafale reportedly losing ground to Super Hornet in Indian Navy competition". Aviacionline. 30 May 2022.
- ^ "MMRCA 2.0 Contenders". sps-aviation.com.
- ^ "Indian MoD approves order for 26 Rafale Marines from France". 14 July 2023. Retrieved 14 July 2023.
- ^ Menon, Adithya Krishna (14 July 2023). "India to Procure Rafale M, More Scorpene Submarines". Naval News. Retrieved 14 July 2023.
- ^ jacek. "Poland launches program Harpia to procure new multirole combat aircraft". Archived from the original on 27 November 2017. Retrieved 23 November 2017.
- ^ jacek (22 December 2017). "Five companies interested in Polands next generation fighter program Harpia". Archived from the original on 23 December 2017. Retrieved 22 December 2017.
- ^ Siminski, Jacek (5 June 2019). "Poland sends request to buy F-35". Defence News.
- ^ "Boeing withdraws Super Hornet from Swiss contract race" Archived 1 February 2014 at the Wayback Machine. Flightglobal.com, 30 April 2008. Retrieved: 16 August 2013.
- ^ Copley, Caroline; Williams, Alison (18 May 2014). "Swiss voters narrowly block deal to buy Saab fighter jets: projection". Reuters. Zurich. Archived from the original on 20 January 2018. Retrieved 20 January 2018.
- ^ Sprenger, Sebastian (27 March 2018). "Switzerland names contenders in $8 billion 'Air 2030' program". DefenseNews. Cologne, Germany. Archived from the original on 28 March 2018. Retrieved 13 April 2018.
- ^ "No more than CHF8 billion for new fighter jets". Swiss Info. 8 November 2017. Archived from the original on 9 November 2017. Retrieved 13 April 2018.
- ^ Johnson, Rueben F (24 October 2018). "Update: Switzerland's Air 2030 plan narrows down options". IHS Jane's 360. Kiev. Archived from the original on 26 October 2018. Retrieved 26 October 2018.
- ^ Sprenger, Sebastian (11 April 2019). "The F-35 and other warplanes descend on Switzerland this spring". Defense News. Cologne, Germany. Archived from the original on 11 April 2019. Retrieved 11 April 2019.
- ^ "Air2030: Bundesrat beschliesst Beschaffung von 36 Kampfflugzeugen des Typs F-35A". www.admin.ch.
- ^ Insinna, Valerie (30 June 2021). "Lockheed's F-35 topples competition in Swiss fighter contest". defensenews.com.
- ^ "Ce qui a changé entre l'échec du Gripen et aujourd'hui". 8 January 2020 – via www.24heures.ch.
- ^ "Swiss government sets sights on F-35A fighter jet fleet". Swissinfo. 30 June 2021. Retrieved 30 June 2021.
- ^ "Les opposants à l'achat des avions de combat F-35 ont déposé leur initiative". rts.ch. 16 August 2022.
- ^ Fernsby, Christian (26 November 2021). "Air2030: Contracts in place in Switzerland for F-35A and Patriot". Post Online Media.
- ^ "Viola Amherd continue de porter la croix des F-35". Le Temps (in French). 16 February 2022 – via www.letemps.ch.
- ^ "Fighter jet purchase "worrying" but legal, says Swiss audit body". SWI swissinfo.ch. 9 September 2022.
- ^ "Kampfjet-Kauf - Staatsrechtler: Bundesrat muss F-35-Initiative nicht abwarten". 23 March 2022.
- ^ "Der Nationalrat gibt grünes Licht für die Beschaffung des F-35". 15 September 2022. Retrieved 16 September 2022.
- ^ "Air2030: Beschaffungsvertrag für die Kampfflugzeuge F-35A unterzeichnet". Federal Department of Defence, Civil Protection and Sport. Retrieved 19 September 2022.
- ^ "Schweiz unterzeichnet Kaufvertrag für F-35". Tagesanzeiger. 19 September 2022. Retrieved 19 September 2022.
- ^ "El Eurofighter, principal candidato para sustituir a los F-18 españoles". Archived from the original on 17 February 2019. Retrieved 5 November 2018.
- ^ "ILA 2022: Spain signs for Halcon Eurofighters". Janes.com. 23 June 2022.
- ^ Cavas, Christopher P. "Navy: Super Hornet rep for problems untrue". Archived 9 February 2009 at the Wayback Machine marinecorpstimes.com, 17 June 2010. Retrieved: 16 August 2010.
- ^ Butler, Amy. "Marines Sign on for F-35C" Archived 18 April 2018 at the Wayback Machine. Aviation Week, 15 March 2011. Retrieved: 18 April 2018.
- ^ Guse, Paul; Carder, Phillip (10 March 2009). "Boeing to Offer Super Hornet for Greece's Next-Generation Fighter Program". Boeing. Archived from the original on 12 March 2009.
- ^ Clark, Colin, "UK May Borrow F-18s For Carriers: F-35Bs May Be Scrapped" Archived 5 September 2010 at the Wayback Machine. dodbuzz.com, 31 August 2010. Retrieved: 1 September 2010.
- ^ Tran, Philip. "UAE May Ditch Rafale: Hornet a Surprise Competitor for $10B Deal". defensenews.com, 13 September 2010. Retrieved: 11 May 2011.
- ^ "Bulgarian Defense Chief Gets Saab Offer on Gripen Fighter Jets". Novinite, 4 February 2011.
- ^ Adamowski, Jaroslaw (15 November 2017). "Super Hornet could be chosen as Bulgaria's next fighter jet by July". Defense News. Warsaw. Archived from the original on 15 November 2017.
- ^ Tsolova, Tsvetelia; Krasimirov, Angel (21 December 2018). "UPDATE 1-Bulgaria ready to choose F-16 fighter jets for its airforce". Reuters. Sofia. Archived from the original on 22 December 2018.
- ^ Grønlie, Rune (21 March 2012). "Dette flyet vil ikke Norge ha". Avisa Nordland. Archived from the original on 21 January 2022. Retrieved 21 January 2022.
- ^ Boeing Still Interested In South Korea’s KF-X Archived 7 February 2015 at the Wayback Machine - Aviationweek.com, 11 December 2014
- ^ Parsch, Andreas (2006). "DOD 4120.15-L — Addendum". Designation-Systems. Archived from the original on 29 December 2010. Retrieved 8 November 2017.
- ^ Kass, Harrison (4 December 2023). "Boeing's F/A-18 Block III Super Hornet Is a Special Fighter Plane". The Runway Air Force. Retrieved 13 October 2024.
- ^ "Boeing awarded contract to deliver 28 Super Hornets to Kuwait". Archived from the original on 2 April 2018. Retrieved 10 June 2019.
- ^ "Boeing completes Super Hornet deliveries for Kuwait". Janes.com. 6 September 2021. Retrieved 5 December 2021.
- ^ Buliavac, Joseph M. "The aircrew of an F/A-18F Super Hornet, assigned to the "Fighting Redcocks" of Strike Fighter Squadron (VFA) 22, wait to launch from Catapult 3 during night flight operations." Archived 27 February 2015 at the Wayback Machine navy.mil, 2 December 2007. Retrieved: 16 August 2010.
- ^ "CSFWP Link." Archived 13 January 2009 at the Wayback Machine lemoore.navy.mil. Retrieved: 16 August 2010.
- ^ "VFA 34 'Blueblasters' return to NAS Oceana after historic deployment". 10 April 2018. Archived from the original on 14 April 2018. Retrieved 14 April 2018.
- ^ Eiman, Mike (1 February 2012). "NASL crash caused by practice mistakes". Hanford Sentinel.
- ^ Geoff Ziezulewicz (23 May 2020). "Inside a fatal Super Hornet crash in Star Wars canyon". Navy Times.
- ^ "Military Plane Crash in Death Valley: One Year Later". NPS News Release. 31 July 2020.
- ^ "R-2508 User's Handbook, 22 May 2022" (PDF). edwards.af.mil. 23 May 2022. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 June 2022. Retrieved 4 June 2022.
- ^ "F/A-18E/F Super Hornet." Archived 9 October 2006 at the Wayback Machine Aerospaceweb.org. Retrieved: 16 August 2010.
- ^ NATOPS FLIGHT MANUAL, NAVY MODEL F/A-18E/F, 165533 AND UP AIRCRAFT (PDF) (Report). Naval Air Systems Command. Archived (PDF) from the original on 31 December 2018. Retrieved 12 February 2019.
- ^ a b NATOPS FLIGHT MANUAL PERFORMANCE DATA, NAVY MODEL F/A-18E/F, 165533 AND UP AIRCRAFT (PDF) (Report). Naval Air Systems Command. Archived (PDF) from the original on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 20 May 2016.
- ^ STANDARD AIRCRAFT CHARACTERISTICS F/A-18E SUPER HORNET (Report). Naval Air Systems Command. March 2001. Retrieved 3 November 2024.
- ^ a b c d e f Selected Acquisition Report (SAR): F/A-18E/F Super Hornet Aircraft (F/A-18E/F) as of December 31, 2012 (PDF) (Report). Defense Acquisition Management Information Retrieval. Retrieved 4 December 2022.
- ^ a b c "F/A-18 Super Hornet". Boeing. Retrieved 7 February 2023.
- ^ "F/A-18F Super Hornet" Archived 12 April 2013 at the Wayback Machine Fighterworld. Retrieved: 20 February 2013
- ^ 1.1 with loaded weight & 50% internal fuel
- ^ "U.S. Navy Confirms SM-6 Air Launched Configuration Is 'Operationally Deployed'". 5 July 2024.
- ^ "F/A-18 Super Hornet Appears With Unprecedented Heavy Air-To-Air Missile Load". 11 September 2024.
- ^ Helfrich, Emma (7 September 2022). "LITENING Targeting Pod Tested On F/A-18 Super Hornet For First Time". The Drive.
Bibliography
[edit]- Donald, David. "Boeing F/A-18E/F Super Hornet", Warplanes of the Fleet. London: AIRtime Publishing Inc, 2004. ISBN 978-1-88058-889-5.
- Elward, Brad. Boeing F/A-18 Hornet (WarbirdTech, Vol. 31). North Branch, Minnesota: Specialty Press, 2001. ISBN 978-1-58007-041-6.
- Elward, Brad. The Boeing F/A-18E/F Super Hornet & EA-18G Growler: A Developmental and Operational History. Atglen, Pennsylvania: Schiffer Publishing, Ltd. 2013. ISBN 978-0-76434-041-3.
- Holmes, Tony. US Navy Hornet Units of Operation Iraqi Freedom. London: Osprey Publishing, 2004. ISBN 978-1-84176-801-4.
- Jenkins, Dennis R. F/A-18 Hornet: A Navy Success Story. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2000. ISBN 978-0-07134-696-2.
- Winchester, Jim. The Encyclopedia of Modern Aircraft. San Diego: Thunder Bay Press, 2006. ISBN 978-1-59223-628-2.
External links
[edit]- Official website

- F/A-18 U.S. Navy fact file Archived 11 January 2014 at the Wayback Machine, and F/A-18 Navy history page
- Boeing F/A-18 Super Hornet page and Super Hornet Aero India briefing on Boeing.com
- Air refueling
- Aircraft first flown in 1995
- Carrier-based aircraft
- Mid-wing aircraft
- Twinjets
- 1990s United States attack aircraft
- 1990s United States fighter aircraft
- Attack aircraft
- Fighter aircraft
- Naval aviation
- Fourth-generation jet fighter
- 4.5-generation jet fighters
- McDonnell Douglas aircraft
- Twin-tail aircraft
- Aircraft with retractable tricycle landing gear
